We are just in the middle of 2023, but it will be known as the year were the mass public has begun accessing and using AI. Whether or not AI will take over a lot of aspects of our life or fall into a more proportional and practical usage is yet to be known.
In this post I’ll try to explain what wheels are turning in the tech industry that drives this revolution and how to jump on this LLM train as well.
How the trend begun
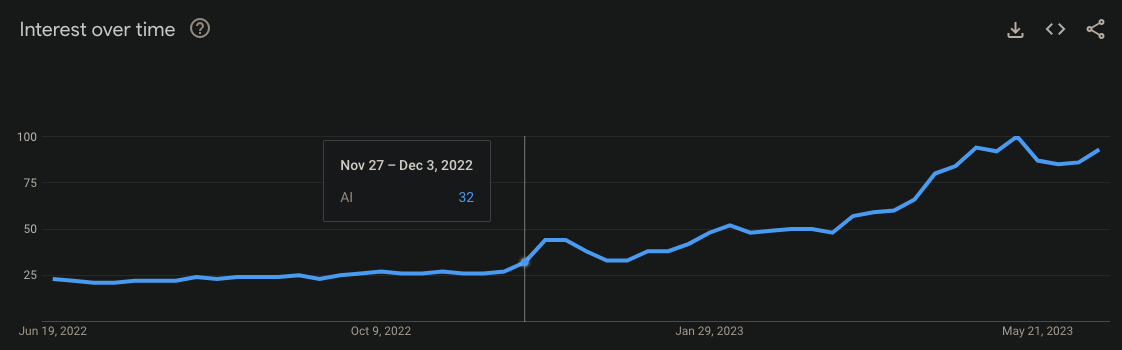
So what started it? ChatGPT was released on November 30, 2022. This is “AI” search popularity on google trends:
Even though AI tech started gaining popularity about a decade ago, ChatGPT was the first product that enabled access to Artificial Intelligence for the mass public. Students began using it for their homework, content writers get its help when writing any piece of long text, and many many more people that are not in tech are now using it.
Other companions to chat AI applications are art-generating apps like DALLE-2 (also from OpenAI, the same creators as ChatGPT), and code-generating apps like GitHub Copilot.
The hype is about Genrative LLMs
ChatGPT isn’t just an “AI”. Artificial Intelligence is a broad term that includes different types of technologies. Specifically, ChatGPT uses a Generative-AI algorithm and an LLM - a Large Language Model. It is under the Machine Learning algorithms umbrella and specifically the Deep Learning (or Neural Networks) models family.
Generative AI means a model is trained to complete the user - the user supplies a prompt, and the algorithm tries to guess the rest. If a user gives a question as a prompt - the model can suggest an answer as a natural continuation of the prompt.
LLMs are just referring to the data type of the content - language. The user “talks” with the model using a natural language, and that is what makes it so compelling to use by everyone - all of us can use a language, and then, suddenly, no training is required to use AI technology.
The first ‘L’ in LLM refers to the size of the model - they are Large. When compared to previous models, ChatGPT made a huge increase in inputs. It was trained on 45TB of data and has 1.5 Billion parameters!
The revolution leaders
Other tech companies have still been developing and using AI before OpenAI - big tech companies like Amazon, Meta, and Google had been working on their own model, and the hype just pushed them to release their models sooner. There are also open-source models getting released frequently on Hugging Face that offer powerful LLMs for everyone to use. All of them are creating and using cutting-edge LLMs and driving the Generative AI revolution
The followers
A lot of tech companies that aren’t AI-driven watched the news about AI. Everyone starts talking about it and discussing how the future is going to change by it.
Therefore, a lot of SaaS products are now getting some AI features embedded in them. In my personal opinion, using AI doesn’t always add additional value to the world, but nonetheless, companies are afraid to miss the train so they piece together AI solutions with their current offering, even if the pieces don’t fit.
AI for everyone
But how do they do it? The big tech companies provide simple API’s so every engineer can access them and use AI in their application. Let’s explore the main concepts to know when trying to integrate to those APIs
Embeddings
Even though we talk to AI chats using natural language, it is still a computer, and computers need numbers to operate, not words. Embeddings are just a numerical representation of the text. The input text goes through tokenization to divide a sequence of text into smaller units, or tokens, such as words, sub-words, phrases, or characters. Then the tokens are passed through the model’s “brain”, and it creates an embedding of the given input.
A good model tries to keep the text’s semantical meaning inside those numbers - the intention of the writer will be kept in a numerical representation. This is where the Intelligence of those models lies.
Similarity
Once the model creates an embedding, we can see it as a vector. We can observe that if the model does its job well, 2 semantically-similar sentences will produce 2 nearing vectors. Common algorithms to measure vector closeness or similarity are Euclidean distance, Cosine, or Dot Product.
Vector DB
The latest buzz in using AI is Vector DBs. If embeddings can create meaningful representations of data, as a user, I want to store representations of my own data. Vector DB gives the ability to store embeddings produced by AI models and search for embeddings similar to them later on, using some similarity search algorithm.
Example
Let’s say we are IKEA customer service engineers, and we want to help our buyers to build their furniture. Really not IKEA style, right?
We want to create a chat where a customer describes where he is stuck in the assembly process, and the chat will answer him on how he should proceed.
We decide to use one of the OpenAI models.
In advance, we collect all the text knowledge ikea has - assembly manuals, all Q&A documents, and previous human customer service conversation transcripts. We query the OpenAI embeddings API to create embeddings from all the knowledge we collected, and we store all the vectors from the responses together with the original texts in milvus vector DB. Now we write the app - a chat server that receives text as input.
- The app will take the input text and query OpenAI API to get an embedding from this text.
- The app will search the vector DB for the top 3 embeddings similar in semantic meaning that might contain the answer to the question.
- The app will take the correlating text and display to the user all of them as optional solutions to the user’s problem
And Voila - we embedded AI in IKEA 🙂
Let’s hope the model works well, and no one will hammer together his nightstand drawers because the chat bot suggested it.
Here is some reference code with a different example.

Comments powered by Disqus.